Apache Kafka integration
Contents
- 1 Compatibility
- 2 Overview
- 3 Configuration
- 4 General Behaviour
- 5 Events
- 5.1 Structure Notification
- 5.1.1 Kafka Message Key
- 5.1.2 Kafka Message Body
- 5.1.3 Additions and Modifications
- 5.1.4 Deletions
- 5.1.5 Kafka Transactions
- 5.1.6 Full Content Publication and Re-synchronisation
- 5.1.7 Not Supported: Subscription to Specific Structures
- 5.1.8 Not Supported: Publication Arbitration on Fusion Registry Load Balanced Clusters
- 5.1.9 Not Supported: Enforcement of Fusion Registry Content Security Rules to Structures Published on Kafka
- 5.1 Structure Notification
Compatibility
| Product | Module | Version | Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fusion Registry Enterprise Edition | Core | 10.0 | Kafka producer supporting 'Structure Notification' events |
Overview
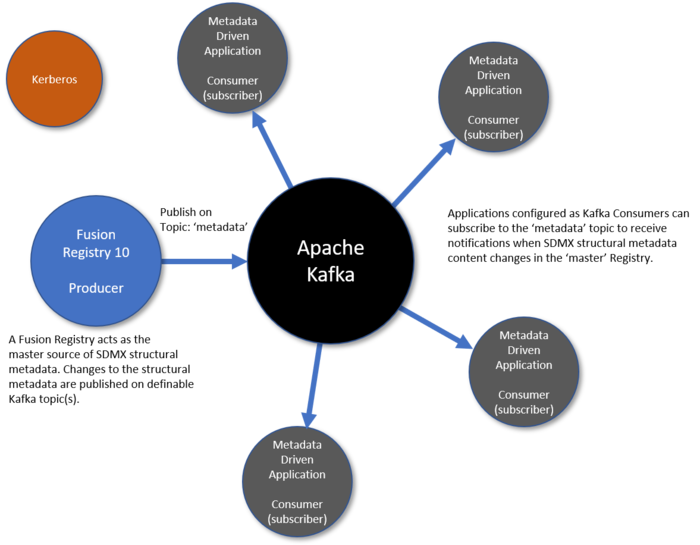
Fusion Registry can act as an Apache Kafka Producer where specified events are published on definable Kafka topics. It consists of a generalised ‘producer’ interface capable of publishing any information to definable Kafka topics, and a collection of ‘handlers’ for managing specific events.
At present there is only one event handler Structure Notification which publishes changes to any structures as they occur, this also include data registrations.
For changes or modifications to structures, the body of the message is always an SDMX structure message. The format is configurable at the event handler level, the structure producer can support any structure output as long as the registry is aware of the VND header, however the UI offers the following choices:
- Fusion JSON (the JSON dialect that pre-dated the formal SDMX-JSON specification)
- SDMX-ML v2.1
Fusion JSON is recommended if the Fusion Registry is being used to support non-sdmx structures (which can not be described in SDMX-ML), for example Reporting Templates and Validation Schemes.
A ‘tombstone’ message is used for structure deletions with the structure URN in the Kafka Message Key, and a null body.
The list of supported events that can be published to Kafka will be extended over time.
Other events envisaged include:
- Audit events such as logins, data registrations and API calls
- Errors, for instance where a scheduled data import fails
- Configuration changes
- Changes to Content Security Rules
Configuration
Configuration is performed through the GUI with 'admin' privileges.
Connection
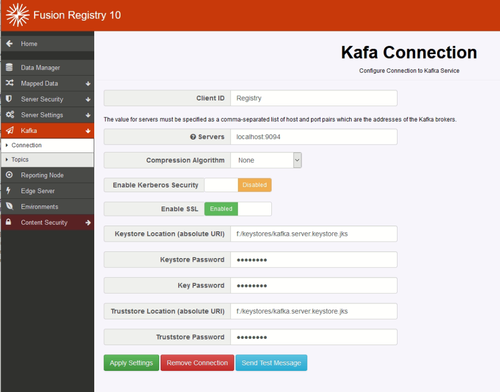
Before Kafka can be used, a connection must be defined the Fusion Registry to a Kafka server (or servers), taking note of the following.
Number of Connections
The Registry supports one connection definition to one or more bootstrap servers. Each server connection can be separated by a comma. The UI displays all connection properties supported by Kafka, and displays the default value that will be used when not explicitly set.
Transactions
Whilst Kafka does not enforce transactions, the Fusion Registry does. A connection will default to using the transaction prefix ‘tx’. The documentation states that this can be null, which is not the case for the Fusion Registry.
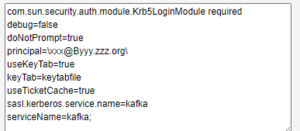
Kerberos
Kerberos integration can be achieved by providing a value for the sasl.jaas.config property. This property expects a new line per configuration setting, in the UI the text area is provided to support multiple lines.
Max Request Size
The connection definition supports the max.request.size property, which will enforce a restriction on the maximum size of the message that can be sent. Additional restrictions for this can be defined on the Kafka server, and the Kafka topic, which are both configured outside of the Fusion Registry. It is important to ensure the server and topic can also handle large request sizes if this property is changed in the Fusion Registry. It is important to note that the max request size refers to the size of the message BEFORE any compression is applied. This is a behaviour of Kafka and cannot be modified. When the message is sent, both the topic and connection will apply the max request size on the compressed message (if compression is enabled) and therefore these can be set to a lower threshold.
Test Connection
The Fusion Registry ensures the bootstrap servers can all be connected to before the connection is saved. However, the test function should be used to ensure the following:
- A message can be sent using the security defined in the connection (e.g. Kerberos)
- Transactions are supported by the connection
- Large messages can be sent with no issue
Note 1: the last test generates a large message (up to the number of bytes specified). As the message contains a lot of repeated text, the compression (if set) will make the final message size very small. If the intention is to also test the message size against the topic and kafka server, then ensure compression is set to none before running the test.
Note 2: The test is run against the applied configuration, remember to apply changes BEFORE running the test.
Topics
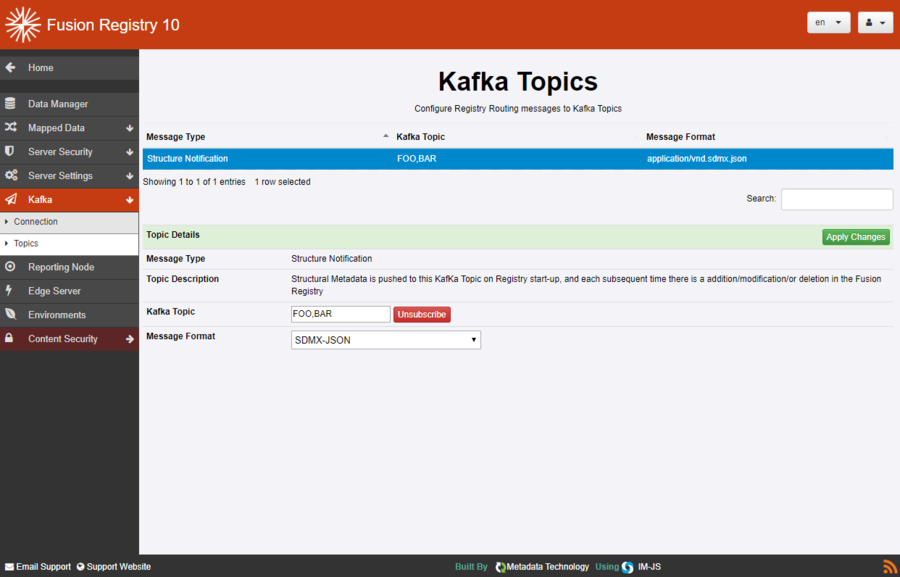
The Topics form allows configuration of which events should be published on Kafka, and on what Kafka Topics.
Kafka Topic is ID of the topic on which to publish.
Each message can be published onto multiple topics by providing a comma separated list of topic names.
So 'FOO' publishes on just the single topic specified.
'FOO,BAR' publishes on both FOO and BAR topics.
The form also allows event specific parameters to be set. For Structure Notification, this is the format of the Kafka Message Body
SSL
It is possible to set up an SSL connection from the Registry to Kafka. It is required that:
- Your Kafka system has been set up correctly with a KeyStore, TrustStore and appropriate passwords
- The Registry has access to both KeyStore and TrustStore
Configuring Kafka for SSL
- Edit the Kafka configuration file: server.properties
- Locate the address for the listeners. This will need to either be changed to support SSL or another port will need to be added. For example, having 2 ports, one for PlainText and the other for SSL can be defined with:
listeners=PLAINTEXT://:9092,SSL://localhost:9093
- Add the following section for your SSL configuration:
ssl.keystore.location = <location of the keystore> ssl.keystore.password = <keystore password> ssl.key.password = <key password> ssl.truststore.location = <location of the truststore> ssl.truststore.password = <truststore password>
For example:
ssl.keystore.location = f:/keystores/kafka.server.keystore.jks ssl.keystore.password = password ssl.key.password = password ssl.truststore.location = f:/keystores/kafka.server.truststore.jks ssl.truststore.password = password
Configuring the Registry Kafka SSL communication
This can be specified on the Kafka Connection page.
Ensure that the "servers" field shows a connection to the SSL port as configured in Kafka.
The following five pieces of information must be known and entered in the appropriate input fields:
- KeyStore Location - the full URI is required
- KeyStore Password
- Key Password
- TrustStore Location - the full URI is required
- TrustStore Password
General Behaviour
Publication Reliability
Message publication is not 100% reliable.
Fusion Registry places event messages as they are created onto an internal in-memory Staging Queue. When a message is created, an immediate attempt is made to publish to the Kafka broker cluster. If the publication fails (the Kafka service is unavailable, for instance), the message is returned to the Queue. An independent Queue Processor thread makes periodic attempts to complete the publication of staged messages.
IMPORTANT: Messages stay on the Staging Queue until they are successfully published to Kafka. However, the Staging Queue is not persistent so any staged but unpublished messages will be lost when the Fusion Registry service terminates.
Each individual event message service manages the risk of message loss in a way appropriate for their specific use case. For Structure Notification, the risk is managed by forcing consumers to re-synchronise their complete structural metadata content with the Registry on Registry startup. Even if structure change event messages were lost, Consumers' metadata is reset to a consistent state.
Events
The following Fusion Registry events are available for publication on a Kafka service.
| Event | Details |
|---|---|
| Structure Notification | Addition / modification or deletion of SDMX structures |
Structure Notification
SDMX Structural Metadata is published to definable Kafka topics on Fusion Registry startup and each time structures are added / modified, or deleted. Metadata-driven applications can subscribe to the relevant topic(s) to receive notifications of changes to structures allowing them to maintain an up-to-date replica copy of the structural metadata they need.
Example use cases include:
- Structural validation applications which require up-to-date structural metadata such as Codelists and DSDs to check whether data is correctly structured.
- Structure mapping applications which require up-to-date copies of relevant Structure Sets and maps to perform data transformations.
Kafka Message Key
The SDMX Structure URN is used as the Kafka Message Key. Consumers must therefore be prepared to receive and interpret the key as the Structure URN correctly when processing the message. This is particularly important for structure deletion where the Message Key is the only source of information about which structure is being referred to.
Kafka Message Body
The Kafka Message Body is a normal SDMX structure message, except in the case of deletions where the message has no content (a null payload), and the structure to delete is identified exclusively by its URN in the Message Key. The format of the SDMX structure message is configurable using the Topics form with the following options available:
| Format | Explanation | HTTP Accept Header Equivalent |
|---|---|---|
| SDMX-ML 1.0 | SDMX-ML 1.0 XML structure document | application/vnd.sdmx.structure+xml;version=1.0 |
| SDMX-ML 2.0 | SDMX-ML 2.0 XML structure document | application/vnd.sdmx.structure+xml;version=2.0 |
| SDMX-ML 2.0 | SDMX-ML 2.1 XML structure document | application/vnd.sdmx.structure+xml;version=2.1 |
| SDMX-EDI | EDI | application/vnd.sdmx.structure;version=edi |
| SDMX-JSON | SDMX-JSON 1.0 | application/vnd.sdmx.json |
| XLSX (flat) | Metadata Technology's Excel structure format | application/vnd.xlsx |
| Fusion-JSON | Metadata Technology's JSON format with similarities to SDMX-JSON provided primarily for backward compatibility | application/vnd.fusion.json |
Events for certain structures will only be published if the structure type is supported by the chosen format. Only Fusion-JSON supports all possible structures including Fusion Registry 'extended structures' like Validation Schemes.
Additions and Modifications
Addition and Modification of structures both result in an SDMX 'replace' message containing the full content of the structures. Deltas (such as the addition of a Code to a Codelist) are not supported.
Deletions
Deletion of structures results in a 'tombstone' message, i.e. one with a null payload but the URN of the deleted structure in the Message Key.
Kafka Transactions
Additions and modifications to structures in Fusion Registry are published using Kafka Transactional Messaging to help guarantee consistency by providing:
- Atomicity - The consumer will not be exposed to uncommited transactions
- Durability - Kafka brokers guarantee not to lose any committed transactions
- Ordering - Transaction-aware consumers receive transactions in the original order
- Non-Duplication - No duplicate messages within transactions
If a single structure is added or changed, the transaction will contain just that structure.
Transactions will contain multiple structures in cases including:
- Where multiple structures are submitted to the Registry in a single SDMX-ML message.
- Where a structure's Agency or ID is changed that affects dependent structures.
Subscribers to the Kafka topic must be transaction-aware, and must ensure that each transaction is processed atomically to maintain the referential integrity of their structural metadata replicas.
Structure deletions are never mixed with additions / modifications in the same transaction. This reflects the behaviour of the SDMX REST API whereby additions / modifications use HTTP POST, while deletions require HTTP DELETE.
Full Content Publication and Re-synchronisation
Under certain conditions, the Fusion Registry Producer will publish all of its structures in a single SDMX Structure Message of the chosen format to Kafka.
These are:
- When a new Kafka connection is set up, or the configuration of an existing Kafka connection is changed
- Registry startup
The principle here is to ensure that Consumers have a consistent baseline against which to process subsequent change notifications.
It also mitigates the risk that changes held in the Registry's in-memory queue of messages awaiting Kafka publication were lost on shutdown by forcing Consumers to re-synchronise on Registry startup.
Not Supported: Subscription to Specific Structures
The current implementation does not allow Kafka Consumers to subscribe to changes on specific structures or sets of structures, such as those maintained by a particular Agency. Consumers subscribing to the chosen topic will receive information about all structures and will need to select what they need.
Not Supported: Publication Arbitration on Fusion Registry Load Balanced Clusters
IMPORTANT: There is currently no arbitration mechanism between peer Fusion Registry instances configured in a Load Balanced cluster. This means that each member of the cluster independently publishes each structure change notification to Kafka, resulting in duplication of notifications.
Structure changes made on one instance of Fusion Registry in a cluster are replicated to all of the others through either a shared database polling mechanism, or by Rabbit MQ messaging. An instance receiving information that structures have changed elsewhere in the cluster updates its in-memory SDMX information model accordingly. The update event is however trapped by its Kafka notification processor and published as normal.
Changes are required to the Kafka event processing behaviour of Registries operating in a cluster to arbitrate over which instance publishes the notification on Kafka such that a structure change is notified once and only once, as expected.
Not Supported: Enforcement of Fusion Registry Content Security Rules to Structures Published on Kafka
Fusion Registry Content Security defines rules restricting access to selected structures and items to specific groups.
The Kafka Structure Notification processor does not enforce Content Security structure rules meaning that all structures are published to the Kafka broker service on the defined topic(s), irrespective of what restrictions may be in place. The risk here is that people or applications that would otherwise not have access to specific structures may be able circumvent the rules normally imposed by Fusion Registry's Content Security sub-system by subscribing to the Structure Notification topic on Kafka. Kafa Streams Security allows control over access to topics. While an all-or-nothing approach of limiting access to all published structures may be sufficient for some applications, it doesn't solve the use case where a consumer should be allowed access to certain structures, but not others.
The Kafka publish-and-subscribe mechanism means that the Fusion Registry producer has no knowledge of who will be consuming the metadata at the point of publication. Up-front decisions therefore have to be made as to what rules to apply when publishing to Kafa. Options include:
- Only publish 'public' structures - i.e. those without any rules restricting access
- Publish changes for each Content Security group (and 'public') on their own separate Kafka topics - applying Kafka Security to the topics would then ensure the intended access restrications are enforced