Difference between revisions of "Codelist V10"
m (→Flat Codelists) |
(→Hierarchical Codelists) |
||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | = | + | =Codelists with Simple Hierarchies= |
| + | <p>SDMX allows simple hierarchies to be defined within flat Codelists by making a code the parent of codes that logically sit under it in the hierarchy.</p> | ||
| + | <p>Imagine a CL_REF_AREA Codelist containing individual codes for each European country, and a code (EUR) for Europe as a whole. A simple hierarchy for Europe can be created by setting EUR as the parent for each of the countries</p> | ||
| + | ==Simple Flat Codelist== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Code ID !! Code Name !! Parent | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | EUR || Europe || (none) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | DE || Germany || EUR | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | FR || France || EUR | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | IT || Italy || EUR | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | GR || Greece || EUR | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | SE || Sweden || EUR | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | AU || Austria || EUR | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PL || Poland || EUR | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
SDMX Codelists allow codes to be organised into hierarchies enabling software tools to display them in a logical tree structure for searching and navigation. Code hierarchies can also be used as part of data consistency check rules where data is considered to be consistent if the sum (or other aggregation) of values for child codes equals the value given for the parent code. | SDMX Codelists allow codes to be organised into hierarchies enabling software tools to display them in a logical tree structure for searching and navigation. Code hierarchies can also be used as part of data consistency check rules where data is considered to be consistent if the sum (or other aggregation) of values for child codes equals the value given for the parent code. | ||
==Simple Codelist Hierarchies== | ==Simple Codelist Hierarchies== | ||
Revision as of 01:51, 19 December 2019
Overview
An SDMX Codelist is a managed list of classification codes.
| Structure Type | Standard SDMX Structural Metadata Artefact |
| Maintainable | Yes |
| Identifiable | Yes |
| Item Scheme | Yes |
| SDMX Information Model Versions | 1.0, 2.0, 2.1 |
| Concept ID | CODELIST |
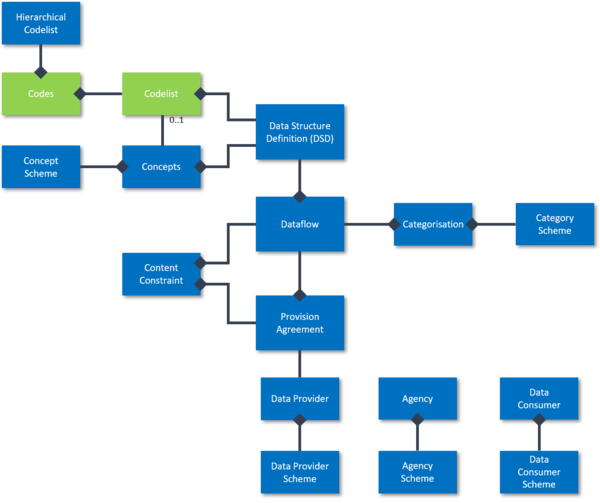
Codelists Context within the SDMX 2.1 Information Model
The schematic illustrates the core artefacts of the SDMX 2.1 Information Model.
Codelists can be referenced directly by Data Structure Definitions, or indirectly through Concepts to describe the list of valid values for enumerated Dimensions or Attributes.
Usage
SDMX Codelists are lists of classification codes used principally for defining the set of allowed values for enumerated Components in Data Structure Definitions (DSDs) or Metadata Structure Definitions which describe Reference Metadata.
Each code is a separate Item so must have an ID and a Name, but can also have an optional Description. While Code IDs must be unique within a Codelist, the same Code ID may be safely used in other Codelists. For instance: The code 'A' may be used in a Frequency Codelist to represent 'Annual', but also appear in an Industry Codelist to represent 'Agriculture'.
Flat Codelists
Flat Codelists are simple lists of codes with no explicit or implied relationships or hierarchies.
Example: FREQUENCY Codelist
| Code ID | Code Name |
|---|---|
| A | Annual |
| S | Half-yearly, semester |
| Q | Quarterly |
| M | Monthly |
| W | Weekly |
| D | Daily |
| B | Daily - Business Week |
| N | Minutely |
Codelists with Simple Hierarchies
SDMX allows simple hierarchies to be defined within flat Codelists by making a code the parent of codes that logically sit under it in the hierarchy.
Imagine a CL_REF_AREA Codelist containing individual codes for each European country, and a code (EUR) for Europe as a whole. A simple hierarchy for Europe can be created by setting EUR as the parent for each of the countries
Simple Flat Codelist
| Code ID | Code Name | Parent |
|---|---|---|
| EUR | Europe | (none) |
| DE | Germany | EUR |
| FR | France | EUR |
| IT | Italy | EUR |
| GR | Greece | EUR |
| SE | Sweden | EUR |
| AU | Austria | EUR |
| PL | Poland | EUR |
SDMX Codelists allow codes to be organised into hierarchies enabling software tools to display them in a logical tree structure for searching and navigation. Code hierarchies can also be used as part of data consistency check rules where data is considered to be consistent if the sum (or other aggregation) of values for child codes equals the value given for the parent code.
Simple Codelist Hierarchies
Simple hierarc
Complex Codelist Hierarchies
Conventions
CL_ Codelist ID Prefix
Codelist IDs are given a 'CL_' prefix to distinguish them from other structures. For instance: CL_FREQ, CL_REF_AREA, CL_AGE.
Code ID Conventions
Codes can take any legal SDMX ID. But there are several conventions that should be taken into account when choosing Code IDs:
| Uppercase Code IDs | By convention, Code ID's are in uppercase such as 'ABC'. Lower case Codes are valid (for example 'abc'), but care should be taken in their use to avoid confusion. |
| '_Z' Code | The '_Z' code is conventionally used for the Undefined and Unknown classification. |
| 'TOTAL' Code | The 'TOTAL' code represents the total or sum of the dimension. For a 'country' dimension, series with TOTAL would indicate the sum of observation values for all countries. |
Examples
Simple Flat Codelist
| Code ID | Code Name |
|---|---|
| A | Annual |
| S | Half-yearly, semester |
| Q | Quarterly |
| M | Monthly |
| W | Weekly |
| D | Daily |
| B | Daily - Business Week |
| N | Minutely |
Flat Codelist with Optional Code Descriptions
| Code ID | Code Name | Code Description |
|---|---|---|
| K | Calendar component | Synonyms: Calendar effects; calendar factors |
| X | Seasonal component | Synonyms: Seasonal effects; seasonal factors |
| M | Seasonal and calendar components | Synonyms: Seasonal and calendar effects; seasonal and calendar factors |
| I | Irregular component | Synonym: Irregular effects |
| N | Neither seasonally adjusted nor calendar adjusted data | Synonyms: Raw data; unadjusted data |