Difference between revisions of "Security Configuration - Overview"
(→Authentication) |
(→Overview) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
* [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OpenLDAP OpenLDAP] | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OpenLDAP OpenLDAP] | ||
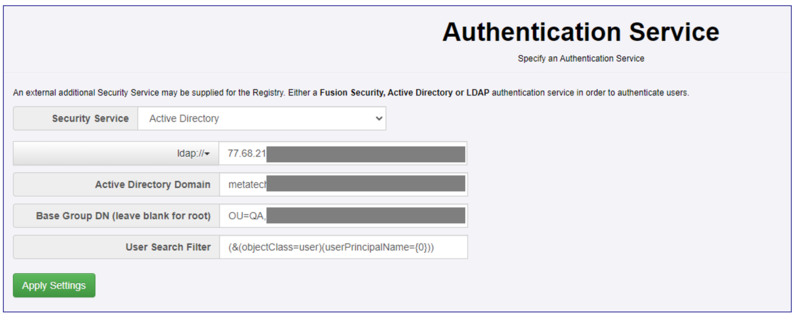
| − | Once a user is Authenticated, the relevant User Account is loaded into the session, and the Registry uses its security model and rules to '''authorise''' the user is allowed to access the resource. The example below shown as example for Active Directory | + | Once a user is Authenticated, the relevant User Account is loaded into the session, and the Registry uses its security model and rules to '''authorise''' the user is allowed to access the resource. The example below shown as example for Active Directory. |
[[File:VMSS0.PNG|Authentication Set-up|800px]] | [[File:VMSS0.PNG|Authentication Set-up|800px]] | ||
Revision as of 05:40, 12 September 2024
Contents
Overview
The Security function is available to logged-in users and found on the Main menu.
Security is split into two distinct functions: User Authentication and User Authorisation. Authentication is the process of ensuring the provided user credentials match up against a valid user account. Authorisation is the process of ensuring a user is allowed to perform the action they are trying to perform.
The Registry only provides Authentication services for one user; the Root user. Authentication for other users are provided by either:
- Fusion Security Web Server (up to FR 10)
- Active Directory using the LDAP protocol
- OpenLDAP
Once a user is Authenticated, the relevant User Account is loaded into the session, and the Registry uses its security model and rules to authorise the user is allowed to access the resource. The example below shown as example for Active Directory.
Authentication
An Authentication Service is required to verify the provided credentials and to supply the Registry with information about the user.
The Registry's web services support HTTP Basic Authentication.
Username and Password authentication requires an authentication service to be running which can be used to verify the credentials. This external authentication service may be Active Directory, [[the two authentication services are mutually exclusive - the Fusion Metadata Registry can only be configured to use one of these services.
After the Authentication process, the Registry must Authorise the user to access the resources. This is achieved by the Fusion Metadata Registry linking the user's account to one or more Organisations, this link is achieved in different ways depending on the Authentication mechanism.
Fusion Security
If the Authentication Service is Fusion Security, then the Fusion Security server will verify the user credentials and return the user account details to the Fusion Metadata Registry, including which Organisations the user belongs to. No additional configuration is required in the Fusion Metadata Registry.
Fusion Security is only applicable for Fusion Registry 10 and is not an option for Fusion Registry version 11.
Active Directory
If Active Directory is used as an Authentication server, then the Common Name (CN) is used to authenticate with the server. The CN is mapped in the Fusion Metadata Registry to one or more Organisations. To learn more about how to map users to Active Directory, please refer to this article.
Authorisation
To understand Authorisation, it is important to understand the security model for the Fusion Metadata Registry. Each user account links to zero or more Organisations maintained in the Fusion Metadata Registry. The Organisation a user account can be linked to falls into one of three categories:
- An Agency
- A Data Provider
- A Data Consumer
A user account may have administrative privileges, which allows the user unrestricted access to any information in the product, including access to the configuration settings of the product.
A Agency user is able to create, maintain, and delete structures that belong to the Agency, or any of its sub-agencies.
A Data Provider user is able to validate and convert datasets the Data Provider has been set up to provide data for via a Provision Agreement.
A Data Consumer user has no special privileges provided by default, however they are able to access the Registry if the product has been set up to enforce login.
Root User
The Registry provides a single root user account, where the credentials are stored locally (not in an external authentication service). The Registry authenticates the root user, and as such the root user is always able to log into the product should the external authentication service become inaccessible.
It is not a requirement to set up an external authentication service - Fusion Metadata Registry can be run in single user mode using the built-in root superuser account. Root user has unrestricted access to the product, and as such security rules do not apply to the root user.
Reporting Template
Restrict Access
Fusion Metadata Registry's default security ensures that generating an Excel workbook from a Report Template is a restricted action. Only users with certain access permission can generate an Excel workbook. The rules are:
| User Type | Permission |
|---|---|
| Admin | Can download Excel Report Workbooks for any Data Provider |
| Agency | Can download Excel Report Workbooks for any Data Provider which is maintained by the Agency |
| Data Provider | Can download Excel Report Workbooks for which they can report data |
| Data Consumer | Can not download any Excel Report Workbooks |
| Anonymous | Can not download any Excel Report Workbooks |
To disable theses default settings, you can use the Enable / Disable button but note it is either all ON or all OFF.
Worksheet Passwords
When a password is applied, when Fusion Metadata Registry generates an Excel workbook from a Report Template definition, it will ensure non-observation cells are locked and can not be edited unless a password is supplied to unlock the worksheet.
This will help prevent the data reporter editing the workbook in such a way to make it unreadable by the Registry.
Passwords are set per Agency and can be changed at any time. If no password is set, the Excel workbook will not be locked.
It is strongly recommended to ensure each agency has a password set to ensure the workbooks are locked.