Difference between revisions of "Concept Schemes and Concepts"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
[[Category:Structural Metadata]] | [[Category:Structural Metadata]] | ||
| − | |||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
Concept Schemes are a container for '''Concepts'''. Concepts are used by '''Dimensions''', '''Attributes''', '''Measures''', and '''Metadata Attributes''' to provide them with a semantic meaning. Concepts can also be used to define a default representation, for example it is possible to link the Concept of Frequency to a Codelist containing all the Frequency Codes, any structure using the Concept will inherit the default representation. | Concept Schemes are a container for '''Concepts'''. Concepts are used by '''Dimensions''', '''Attributes''', '''Measures''', and '''Metadata Attributes''' to provide them with a semantic meaning. Concepts can also be used to define a default representation, for example it is possible to link the Concept of Frequency to a Codelist containing all the Frequency Codes, any structure using the Concept will inherit the default representation. | ||
Revision as of 06:51, 12 September 2023
Overview
Concept Schemes are a container for Concepts. Concepts are used by Dimensions, Attributes, Measures, and Metadata Attributes to provide them with a semantic meaning. Concepts can also be used to define a default representation, for example it is possible to link the Concept of Frequency to a Codelist containing all the Frequency Codes, any structure using the Concept will inherit the default representation.
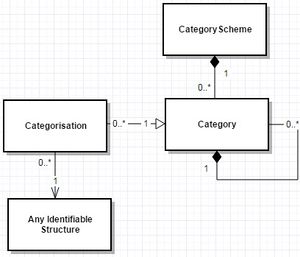
- Figure 1 showing Concepts in a Concept Scheme'
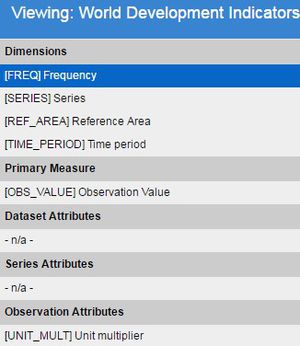
The above shows the Concepts in a Concept Scheme, the image below shows how Concepts are used to give various Components of a Data Structure a name. Concepts can be used by any number of structures, and a structure (such as a DSD) can reference Concepts from any number of Concept Schemes.
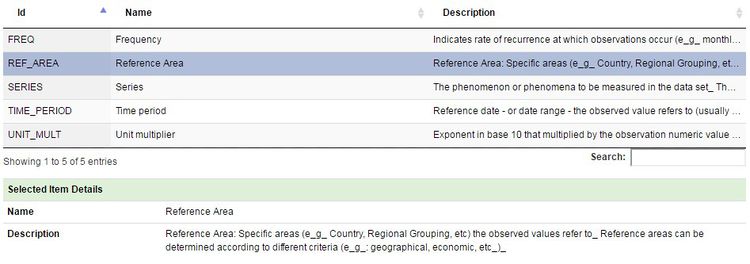
- Figure 2 showing the Concepts used by a Data Structure Definition providing the names and descriptions for each Dimension and Attribute of the Data Structure
Concept Scheme Wizard
The Concept Scheme Wizard includes the first generic step for information about the Concept Scheme.
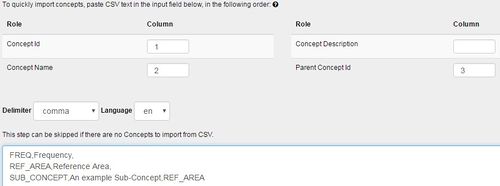
The second step allows the user to import Concepts from CSV. CSV text can be copied and pasted into the text field provided. On clicking ‘Next’ Concepts will be created based on this CSV and added to the Concept Scheme.
- Figure 3 showing an example CSV for Concepts in a Concept Scheme
When importing Concepts it is important to note that the following:
- Concepts will be added to the Concept Scheme, and therefore this step can be used to add additional Concepts to an existing scheme.
- The import language for the name and description fields is defined in the drop down list above the text area.
- If a Concept already exists it will be modified based on the information supplied in the CSV. Modifications include addition of a name or description in a new language into an existing Concept.
- Sub Concepts can be created by using parent Concept Id field. This is shown in the image above where SUB_CONCEPT is a sub-concept of REF_AREA.
- The same number of delimiters are required for each line, even if there is no information for the field, shown above where Frequency includes an additional comma followed by no text (there is no Parent Concept Id).
- If a field contains the delimiter (for example if a name includes a comma) then the text can be put in double quotes.
The third step is to manually add, edit, and delete Concepts.
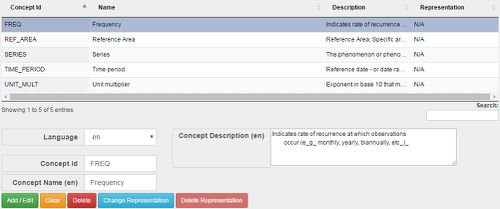
- Figure 4 showing wizard step 3, the manual editing of Concepts
Each Concept can be assigned a default representation. This representation is inherited by Components of a Data Structure Definition (DSD) as a default. Default representation can be overridden by each Component of the DSD if required. To apply a Representation to a Concept, select the Concept in the table, and click the Change Representation button.
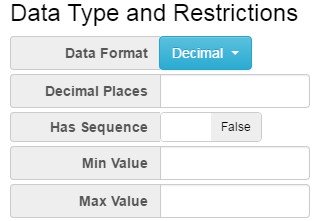
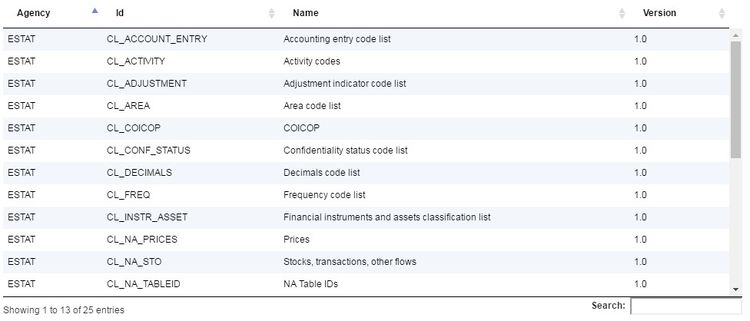
Representation can be non-enumerated or enumerated. Non-enumerated formats refer to data formats which are restricted by data type as oppose to enumerated representation which provide a list of allowed values. Non-enumerated format includes types such as String, Integer, and Decimal, amongst others. Each non-enumerated format can optionally provide additional details relevant to the selected format, such as min/max length for String. Enumerated formats allow a Concept to be linked to a Codelist. The Codelist is used to define the enumerated list of all the allowable values for the Concept.
- Figure 5 showing an example non-enumerated representation form
- Figure 6 showing the list of Codelists that could be assigned to a Concept
The final step of the Wizard allows the user to organise the Concepts into a Hierarchy using drag and drop.