Difference between revisions of "Anatomy of the Data Browser"
(→Quick Filter) |
(→Advanced Filter) |
||
| Line 211: | Line 211: | ||
On each code section, the information on number of series matches, and which codes remain available, is provided by the availableconstraint API. | On each code section, the information on number of series matches, and which codes remain available, is provided by the availableconstraint API. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==SDMX UI Typescript == | ||
| + | The '''CodePicker''' widget is used to build the advanced filter. The input is the current DataQuery as a Object, URL or simply just the Dataflow with no query state. | ||
| + | |||
| + | let config: CodePickerOptions = { | ||
| + | id: "#codepicker", | ||
| + | height: 950, | ||
| + | input: query, | ||
| + | type: CodePicker, | ||
| + | displayOutputOptions: false, | ||
| + | displayTimePicker: false, | ||
| + | displayAggregationOption : false, | ||
| + | dataCallback: (dataSet:DataSet) => void { | ||
| + | //do something | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | let codePicker: CodePicker = UiWidget.build(config) as CodePicker; | ||
| + | |||
| + | To execute the query: | ||
| + | |||
| + | codePicker.executeQuery() | ||
= Series Details = | = Series Details = | ||
Revision as of 13:01, 3 May 2020
Contents
Overview
The Fusion Data Browser is simply a User Interface on top of Fusion Registry / Fusion Edge Server web services. When a user clicks on a link, it calls a web service and renders the response. It makes use of a great third party charting libaray, AmCharts to render the charts, all other code is built in house written in written in TypeScript) which transpiles into JavaScript.
This page takes your through the process and web service calls which are used to build the Fusion Data Browser, if you want to build your own Data Browser you can use the knowledge of what is possible to help.
Behaviour
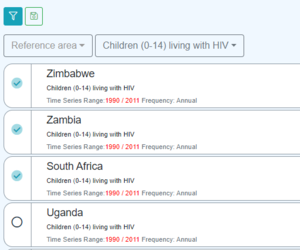
The dataset navigation menu, shown on the left pane of the data browser, was arguably the most complex part of the data browser to build. The Dataset Navigation menu provides a breakdown of datasets by Dimension Id, for example Datasets by COUNTRY. In order to answer this question we need knowledge of:
- What Data Structure Definitions (DSDs) support a COUNTRY Dimension
- What Codelists are used for each of the above DSDs as they may not be the same
- What Codes in the Codelist have data, and for which DSD
The second level of complexity is that the Dataset Navigation component supports a hierarchy of breakdowns, so I can have COUNTRY followed by AGE – the sidebar will then show all the countries that have data, when a user expands a country it will show all the age ranges that have data for the selected country, when an age range is expanded, the user is shown all the Datasets that have data for the selected Country and Age range.
To solve this problem, the sidebar needs access to the following structural metadata:
- All Dataflows
- Data Structures for the Dataflows
- Concepts for the Datastructures
- Codelists
However, in order to minimise response side, we only want Dataflows that have Data, and we only want Codelists with the codes in that are known to have data. Furthermore, we need to know, for each Code, which dataset it has data for.
Web Service
The required information is not possible from the structure API, instead we turn to the availableconstraint API, whose job it is to provide all the above information for a Single Dataflow. This was a problem as we needed the information across all dataflows, so in this instance we extended the availableconstraint API to support this question for All Dataflows.
availableconstraint/all/all?references=descendants&mode=available
The availableconstraint API returns a Content Constraint which tells us which Code Ids are valid for each Diemsion. As there is a Content Constraint per Dataflow, we now know for each Dataflow, evey Code that has data and which Dimension the data is relevent for. This is useful as some Dataaflows use the same Codelist for different Dimensions, Reporting Country and Counterpart Country may both use the same Country Codelist for example (but this does not mean the same code ids have data for both Dimensions).
The references=descendants query parameter is used as it provides the Data Browser with all the supporting metadata used to organise and provide human readable labels to the information from the Content Constraints. The supporting metadata includes the Dataflows, DSDs, Concepts, and Codelists.
We now have enough information to answer all the questions required to build the first level of the sidebar, for example breakdown by Country.
We do not have enough information to build the second part of the hierarchy if there is a second Dimension chosen in the breakdown, this is because whilst we know that a particular Age Range has data for a particular Dataset, we do not know if it has data in the context of the selected Country. It is not efficient to get this information up front, as the more Dimensions in the hierarchy, the number of permutations become too high to realistically solve efficiently. So instead, the information on what comes next is acquired at the time the information is needed (when the user expands the hierarchy). It does this by issuing the query:
https://demo.metadatatechnology.com/FusionRegistry/ws/public/sdmxapi/rest/availableconstraint/all,all,all/;CURRENCY=ARS/all/FREQ?&mode=exact
Again, this is an extension of the availableconstraint query, this time a question is given across all Dataflows, but the question fixes CURRENCY to ARS using matrix parameters, and we only care about the response in the context of the FREQ Dimension. In addition the mode is set to ‘exact’ what this translates to is:
"Tell me what Code Ids have data for the FREQUENCY Dimension across all Dataflows when CURRENCY is ARS"
As this URL does not request descendants, the response this time only contains Code Ids, no other supporting metadata (Dataflows, DSDs, Codelists). This is enough information for us to build the next level of the hierarchy, as we already have the supporting metadata from the first request, in order to know what the corresponding code labels are.
SDMXUI TypeScript
SDMX UI suppoorts the above use case with the DataflowContext object. On initialisation it queries for all the required metadata (Dataflows, DSDs, Codelists) which is cached and used for the remainder of the users data browsing experience.
DataflowContext.loadContext().then(async function (ctx: SDMXUI.DataflowContext): Promise<void> {
//Context is loaded
//Get folder structure used to build sidebar
let folder: ISeriesCatalog = ctx.getSeriesCatalog(["COUNTRY", "AGE"]);
}
Free Text Search
Search By Dataflow and Code
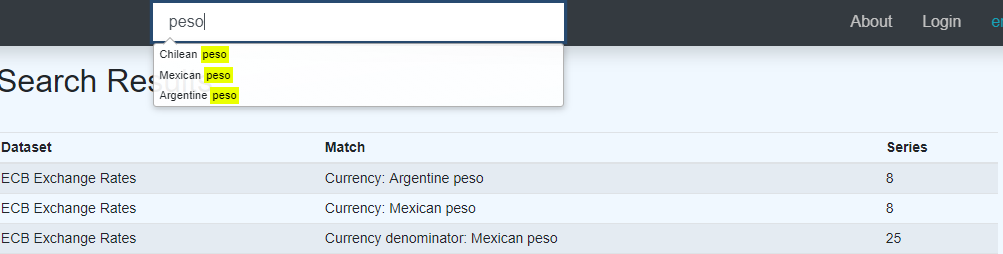
The Free Text Seach feature is very easy to implement, as it simply makes use of the free text search API. There are 2 aspects to the search
- AutoComplete
- Search
The Autocomplete is achieved using the datasearch API with query=[term] and setting auto=true
https://demo.metadatatechnology.com/FusionRegistry/ws/public/datasearch?auto=true&query=peso
To execute the query, simply set auto to false, or exclude it from the URL
https://demo.metadatatechnology.com/FusionRegistry/ws/public/datasearch?query=peso
The search API returns the hits broken down by Dataflow, and then if applicable, by the Classifications that matched grouped by the Dimension or Attribute to which they belong. So is very easy to render.
Search By Series Code
There is a secondary feature, and API to support the feature, and this is to support searching series by seies code. Each series has a unique identifier, which is made up of the code ids for each Dimension of the Data Structure it belongs to. For example Frequency=Annual, Currency=Chinese yuan renminbi, etc, starts to build up a series code of A.CNY.[and so on]. The Fusion Data Browser shows each series code when a series detailsa are expanded in the Series List view. An example of a series code is A.CNY.EUR.SP00.E and this can be used in the following query:
ws/public/seriessearch?query=A.CNY.EUR.SP00.E
The series API allows keys to be wildcarded, as so:
ws/public/seriessearch?query=A..EUR.SP00.E
The returned list of series ids can be coupled with the information from the metadata already obtained to build the Dataset Navigation in order to render the results.
SDMX UI TypeScript
The Typescript makes use of the DataSearch widget with the configuration passing in the callback functions which are used to build the table of results.
let config: SearchOptions = {
id: "#searchInput", //Id of the input element to make the search control
dataSearchApi: Context.INSTANCE.apiList.DataSearchAPI,
seriesSearchApi: Context.INSTANCE.apiList.SeriesSearchAPI,
dataSearchResult: function (searchTerm: string, searchResult: DataSearchResults): void {
},
seriesSearchResult: async function (searchTerm: string, searchResult: SeriesSearchResults): Promise<void> {
},
type: DataSearch,
width: 300,
autocompleteTimeout: 5000,
placeholder: "Search"
};
UIWidgets.INSTANCE.dataSearch = UiWidget.build(config) as DataSearch;
To render the resules we can use the DataflowContext to lookup the metadata
let ctx: IDataflowContext = DataflowContext.INSTANCE;
let results = searchResult.results;
for (let currentResult of results) {
let flow = ctx.getDataflow(currentResult.Dataflow);
...
}
Series List
The primary goal of the Fusion Data Browser is to get the user to the point where they have a list of Series that matches their search or navigation criteria. This can be very simple to achieve, for example when the user uses the Dataset Navigation sidebar, they are essentially building a SDMX REST query by selecting which filters to apply to a Data Query. The outcome of the Navigation bar, is a single Dataflow is selected with zero or more Dimensions being filtered, each Dimension only has 1 filter applied.
Series List From Basic Query Filters
So for example for Exchange Rate data -> Argentine Pesto -> Annual Frequency, the URL query would be the following:
data/ECB,EXR,1.0/A.ARS....
However, as we only want to show the series information, we do not need every observations for each the series. We do want to display the last observation date and observation value, so we will ask only for the last observation to be included:
data/ECB,EXR,1.0/A.ARS....?lastNObservations=1
This is the simple case. What about the case where the query is far too large, Census hypercubes for example can contain millions of series. When the data is too large, a maximum series limit is requested:
data/ECB,EXR,1.0/all?lastNObservations=1&max=200
This tells the server to execute the query by only output the first 200 series. There is no way to define how series are ordered, so the first 200 series does not guarentee in which sequence the series will come back.
Whilst the Fusion Data Browser does not include pagination, this could have been achieved using the offset parameter:
data/ECB,EXR,1.0/all?lastNObservations=1&max=200&offset=200
Series List From Search Result
The series list from a search result uses the same technique as the basic query filters, as the search result provides the Dataflow identifier, and if there is a 'hit' for a classification, then the Dimension and Code Id is also provided. This enables the query to be built using exactly the URL with Dataflow and query filter.
Series List From Series Basket
The Series Basket enables a user to hand pick one or more series, to save these as a basket which can be reloaded at a later date. Furthermore, the basket can contain series from different Dataflows.
Whilst some series baskets can be resolved using the REST URL to GET the data, this is not useful in all situations. Instead a JSON query can be POSTED to the web service. The POST contains the details about the Dataflow, Series List, and other parameters are included such as lastNObservations.
{
"queries": [
"dataflow": {
"id": "GCI",
"agencyId": "WB",
"version": "1.0"
},
"lastNObservations": 1,
"series": ["GHA:EOSQ071:RANK:A","GHA:EOSQ071:ONE_SEVEN_BEST:A","AUS:EOSQ071:RANK:A"]
]
}
As this syntax can contain multiple queries, it supports series baskets from mixed Dataflows.
SDMXUI TypeScript
The SeriesList component is used to build the series list. The dataset parameter can takes a JSON Data Query or REST URL (amongst other things)
let seriesListConfig: SeriesListOptions = {
seriesTitle: "${CURRENCY} to ${CURRENCY_DENOM}",
seriesSubtitle: "${EXR_TYPE}",
seriesFooter: "Time Series Range:${T} Frequency: ${FREQ}",
limit: 200,
id: "#series-list-div",
height: 900,
type: SeriesList,
dataset: dataset,
resolveLabel : key => { return LocaleUtil.getLabel(key);},
onBuild: async function (widget: UiWidget): Promise<void> {
//Series List has been built 'widget' is the built SeriesList
},
showPch:false,
seriesSelect: (chart: ASeriesChart, series: Series) => {
//User has Selected a series
},
seriesDeselect: (chart: ASeriesChart, series: Series) => {
//User has deslected the series
}
};
UiWidget.build(seriesListConfig);
Quick Filter
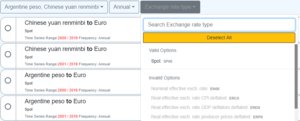
The quick filter is a very easy problem to solve using the SDMX availableconstraint query. This query, which is also used for the Dataset Navigation solution, is used to request a list of Code Ids which remain valid based on the current query state. As we already have the supporting metadata, all we need are the code ids, not the code labels.
availableconstraint/ECB,EXR,1.0/A.ARS+CNY....?mode=available
There is one important thing to note with this query, and that is the mode=available. In the navigation menu this was set to ‘exact. Mode actual is requesting a list of code ids that would come back in the response if we were to execute the query now. Mode actual is requesting the code ids which remain valid selections even if they are not in the response.
The SDMX wiki provides full details on this important distinction. In this use case we want to present the user with a list of codes that remain available selections and disable to code ids that no longer remain valid based on the current query state.
The response to this query provides all the information required to update the quick filters accordingly.
SDMX UI TypeScript
The Series List Component provides the functions to ask what filters are available for each Dimension, so the Quick Filters are lazy loaded (filters are obtained when the user expands the drop down).
let availableSelections:IAvailableData = await seriesList.getUserFilteredAvailableData(); let selectedCodes = await seriesList.userFilteredDataQuery.getCodeSelections(dimId); let validCodes = availableSelections.validcodes[dimId];
Advanced Filter
The advanced filter is an extension of the quick filter, and makes use of the same availableconstraint API to get the information back. However, other then aspects which are solved in the user interface such as search and select all, there is one more feature which requires more information from the metadata. The extra feature is displaying the Codelist as a Hierarchy. This metadata already exists from the original query to build the Dataset Navigation menu, the information is in the Codelist response as each Code can reference a single parent by Id.
If we wanted to provide more complex hierarchices or different hierarchical views, we could have queried for Hierarchical Codelists which use the Codelist we are displaying.
On each code section, the information on number of series matches, and which codes remain available, is provided by the availableconstraint API.
SDMX UI Typescript
The CodePicker widget is used to build the advanced filter. The input is the current DataQuery as a Object, URL or simply just the Dataflow with no query state.
let config: CodePickerOptions = {
id: "#codepicker",
height: 950,
input: query,
type: CodePicker,
displayOutputOptions: false,
displayTimePicker: false,
displayAggregationOption : false,
dataCallback: (dataSet:DataSet) => void {
//do something
};
};
let codePicker: CodePicker = UiWidget.build(config) as CodePicker;
To execute the query:
codePicker.executeQuery()